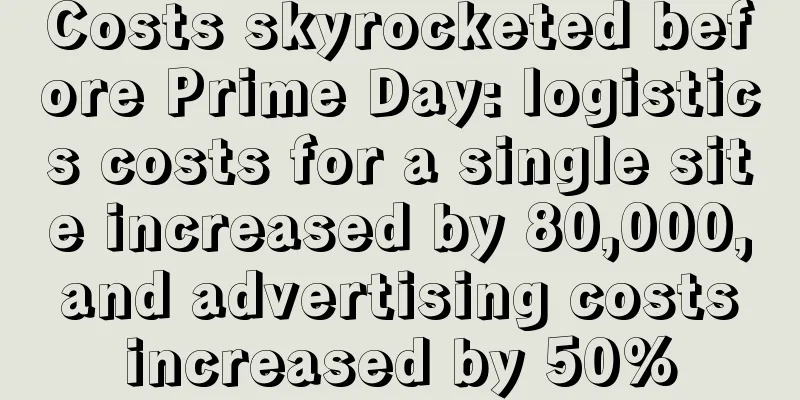|
ChatGPT, which emerged at the end of 2022, was like an arrow that broke through the ecosystem of thousands of industries in an instant, thus setting off a dramatic change in the name of AI transformation. AI can deeply learn and mine massive amounts of data in a short period of time, and then use complex algorithm models to quickly analyze and process data - this can be used to predict industry development trends, gain insight into market demand curves, or provide accurate digital solutions. In a nutshell, its core value lies in achieving the ultimate goal of reducing costs and increasing efficiency by leveraging efficiency, which is highly consistent with the cross-border e-commerce industry under the huge wave. At this stage, the cross-border industry is at an important bottleneck of brand refinement transformation . Cost reduction, efficiency improvement, and digital upgrading have also become the development keywords for overseas companies. As artificial intelligence continues to penetrate the cross-border field, what role does it play? How can overseas companies transform this emerging productivity into specific sales competitiveness? AI cross-border boom in the first year Before ChatGPT was launched, we had already experienced the power of artificial intelligence in many niche areas. But it was not until ChatGPT was born as a general production tool that AI really entered the lives of the general public, integrated into thousands of industries, and even cross-border e-commerce - the first year of AI cross-border is booming. The 2023 Cross-border E-commerce Workplace Status Survey Report shows that among all respondents, 33% of cross-border companies are using ChatGPT, and nearly 15% of companies are expected to put it into use. To date, ChatGPT has been widely used in multiple scenarios. Perhaps actual data can better illustrate the effectiveness of this AI tool in cross-border operations. As one of the earliest cross-border companies to try it out, Jihong Holdings has achieved the operational results shown in the figure through ChatGPT.
It is not difficult to see from the case of Jihong Co., Ltd. that AI can almost empower the entire chain from pre-sales to sales and after-sales. In particular, it can replace some repetitive work that lacks technical content, which has largely liberated more operational productivity. Therefore, after AI tools represented by ChatGPT became a new weapon to leverage efficiency growth, major e-commerce platforms began to get anxious. In May, eBay quietly launched an AI-based description generator in its Android application. After sellers enter specific product attributes, a description text will be automatically generated. However, the tool is still in the early testing stage, so there are still many limitations, such as automatically clearing the original text, descriptions that do not match the actual product, and generated content that is too lengthy and lacks highlights. At the same time, Lazada launched an AI chatbot called LazzieChat , powered by OpenAI ChatGPT technology. Compared to eBay's approach from the perspective of assisting sellers in operations, LazzieChat chooses to focus on optimizing the consumer experience, which is equivalent to playing the role of a 24-hour online customer-exclusive shopping guide. By deconstructing user needs, it can quickly provide personalized suggestions and product recommendations. On the other hand, Amazon, the leading e-commerce company, has been involved in the field of AI for a long time, but has rarely deployed the application of generative AI. Not wanting to be left behind, Amazon has been madly competing for this trend in three directions in recent months: serving itself, serving the public, and serving sellers. Whether it is transforming AIGC into internal productivity or creating AI products for the general public, Amazon seems to have gradually taken a leading position. However, in terms of e-commerce empowerment, it is still in its infancy. On August 14, Amazon officially announced the launch of a product review summary feature based on generative artificial intelligence, which provides a short summary on the listing product details page, focusing on summarizing the attributes and characteristics of the products sold, thereby guiding consumers' purchasing decisions. At the same time, Amazon has launched a small-scale test for an AI generation tool: when sellers add new products, by entering a set of product-related keywords, detailed information such as listing titles, descriptions, and key points will be automatically generated. Regarding the application of AIGC in the field of e-commerce, major platforms have chosen to look for breakthroughs in two directions: one is to optimize consumer experience, and the other is to assist sellers in operations. But it is obvious that they all have common flaws: the functions are relatively primitive and single, and lack innovation. At this stage, ChatGPT can already play an important auxiliary role in multiple links such as product selection and development, graphic editing, and even brand marketing. In contrast, the AI tools developed by e-commerce platforms are far from enough to meet the operational needs of merchants. AI breaks the deadlock in traditional cross-border cost reduction era Under the huge wave of AI, the cross-border e-commerce industry is also brewing a profound change: the grassroots model of violent distribution and traffic-oriented is gradually becoming an outcast of the times, and madly sweeping the supply chain and reaching the brand end is becoming the new law of the jungle. In the past, Chinese merchants seized the opportunity of the traffic dividend of the times, followed the geographical advantage of the cheap supply chain, and used cost advantage as the underlying logic to form a set of risky and radical pirate tactics that subverted the rules - increasing sales and faking orders. However, the outbreak of account bans and the pressure of the external environment have jointly defeated this system, accompanied by increased uncertainty in various sales links and rapidly rising costs. As the traffic dividend recedes and the torrent of low-price competition surges in, a new turning point in development has arrived unexpectedly: reducing traffic costs and increasing operational efficiency. Today, the strong entry of AI has rewritten the rules of the game. Whoever can understand the cross-border use of AI will be able to seize the initiative in this battle to reduce costs and increase efficiency. Cross-border expansion is a long-term battle. The entire operation chain is huge and complex, covering product development, supplier procurement, marketing promotion, logistics fulfillment, and after-sales service. Behind the long sales front are closely linked costs: logistics and transportation, internal and external traffic, platform commissions, and human resource management. According to iResearch Consulting data, platform commissions, advertising and marketing, personnel management and other miscellaneous costs of cross-border e-commerce brands account for about 65% of the core costs. In other words, the so-called AI cost reduction and efficiency improvement is to integrate it into the key nodes of creating these costs. Specifically, the application scenarios of AI in the cross-border e-commerce industry can be roughly divided into three levels: logistics management, sales operations, and traffic promotion. Under the generative artificial intelligence craze led by ChatGPT, the era of AI empowerment has exploded across borders in two major scenarios: sales and promotion - as a new type of low-cost productivity and a low-threshold traffic entrance. The facilitation of cross-border transactions is accompanied by the generation of massive amounts of complex data and content production needs. The power of AI lies in its efficient means of matching information with demand. It can not only quickly process data and mine correlations, but also collect and produce content based on this data. Taking product selection and development as an example, it often goes through several major processes: 1. Target market research: geographical environment, cultural characteristics, and localization policy 2. Consumer demand insights: hot-selling categories, user profiles, and market demand trends 3. Product development: product features, core selling points, specific pricing, target groups, market assessment In the process of manual product selection, complex factors such as language barriers, cultural barriers, and market fluctuations often increase the time and uncertainty of product selection. Furthermore, humans are not machines, their energy is limited, and mistakes are inevitable. It is inevitable to rely on more accurate tools to improve the error tolerance rate. With the support of AI technology, sales strategies can be adjusted in a timely manner based on AI's analysis of user clicks, product conversion rates, market feedback and other data, thereby increasing the rate of creating hits. This can also help shorten the product selection cycle and significantly save labor efficiency.
Cross-border sales are like a long-lasting marathon battle. In addition to product endurance, time and cost are also the key to victory. The former means grabbing the first-mover advantage of products and occupying the market opportunity, while the latter represents a wider profit space. Who will be eliminated by AI? In the history of the development of artificial intelligence, there is a famous milestone event - the AI robot AlphaGo defeated the world champion of Go, Lee Sedol. Behind this battle of the century, humans deeply felt the despair of being surpassed by artificial intelligence and being far behind. Now that the AI wave led by ChatGPT has swept through thousands of industries, it is inevitable that many people will once again feel a similar sense of panic. When AI takes on content production tasks such as painting, writing, and video production, and upgrades at will with its powerful learning ability, will it eventually completely replace human labor at some point in the future? When the ChatGPT virus first started ravaging the cross-border industry, anxiety that "a large number of Amazon operators might lose their jobs" was also spreading. Indeed, with the in-depth application of AI in the cross-border industry, basic positions with low technical barriers and more repetitive labor are likely to be abolished. It is reported that after independently developing an AI management system, Yibai Network has effectively improved the operational efficiency and unit labor efficiency of core business links. From the end of 2020 to March 2023, through system-assisted manual labor, about 400 basic sales personnel have been optimized. However, the balance between gains and losses is a potential law, and at the same time, AI also creates new opportunities. How to maximize the imagination of AI and how to deeply integrate AI with cross-border operations, such trends will also drive a broader demand for talent. In fact, AI is not perfect. There are potential risks, including limitations in training models, insufficient ability to analyze complex problems, and data privacy leakage. But more importantly, AI has no emotions and lacks creativity. AI does not have the problem of limited energy. It can act as a perpetual motion machine that works 24 hours a day, constantly analyzing data, calculating results, and providing solutions. However, AI's aesthetic level and judgment ability are difficult to compare with humans. AI produces content quickly and efficiently, but the specific effects and how to apply them are ultimately in the hands of humans. As an assistant, AI can perform basic work of process standardization, but it cannot completely take over the main business. AI generation, human integration, understanding, and decision-making can save time and improve efficiency, while allowing operators to devote more energy to higher-level business links such as product strength building and brand building. A foreseeable development trend is that more explicit expression of content needs, more precise use of AI, and deeper understanding of AI will become the mainstream in the future. Rather than saying that AI empowers people, it is better to say that people give AI a wider range of application space. |